Blue Carbon in the ROPME Sea Area
Blue Carbon is carbon captured and stored in the marine environment.
The ability of blue carbon ecosystems to remove CO2 from the atmosphere means that they play an important role in climate change mitigation. Tidally influenced coastal ecosystems are particularly efficient at the capture and long-term storage of carbon.
Blue carbon ecosystems also provide a range of benefits that are essential of climate change adaptation, including coastal protection and food security.
Despite their importance, blue carbon ecosystems are being degraded and lost at an alarming rate. Damage to these ecosystems results in the reduction or loss in their carbon capture ability and can lead to the release of carbon back into the atmosphere.
The ROPME Sea Area is a host to a diverse set of blue carbon ecosystems including mangroves, seagrass, and saltmarshes along with coastal sabkhas (salt flats) and microbial mats.
Effective management strategies are required to protect, restore and expand blue carbon ecosystems across the RSA, if the full potential benefits of blue carbon are to be realised.

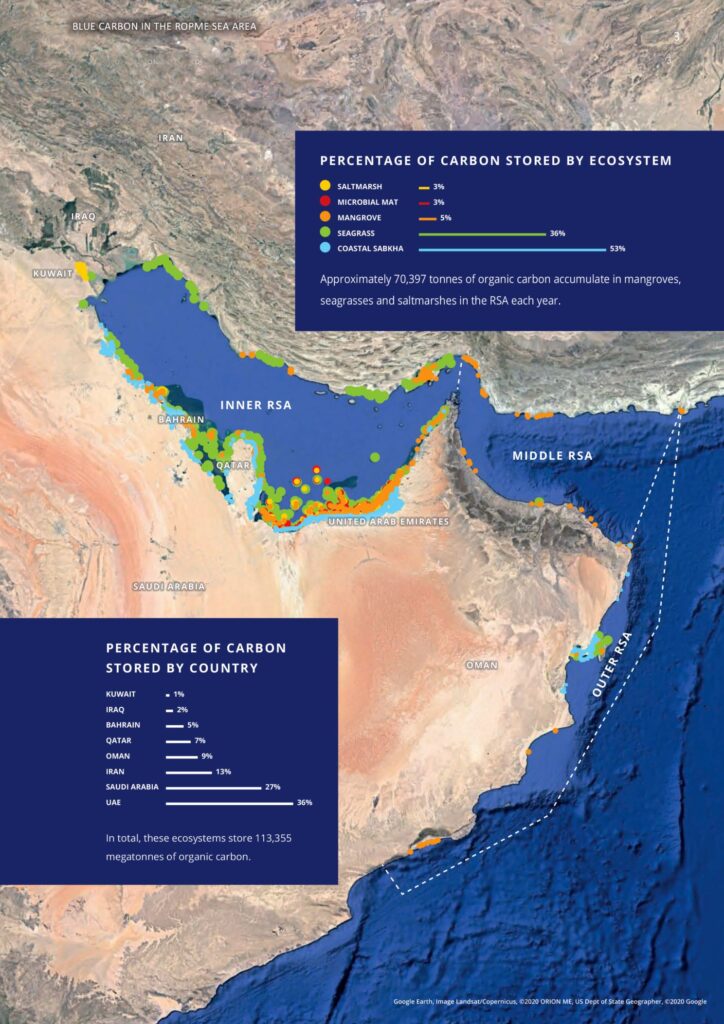
(Extracted from the report ROPME (2020) Policy Brief: Blue Carbon Assessment in the ROPME Sea Area (Howes, E.L. Benson, L., S ,Kröger, Procter, W., Buckley, P., Lincoln, S., and Le Quesne, W.J.F., Cefas, Lowestoft, 4pp.)